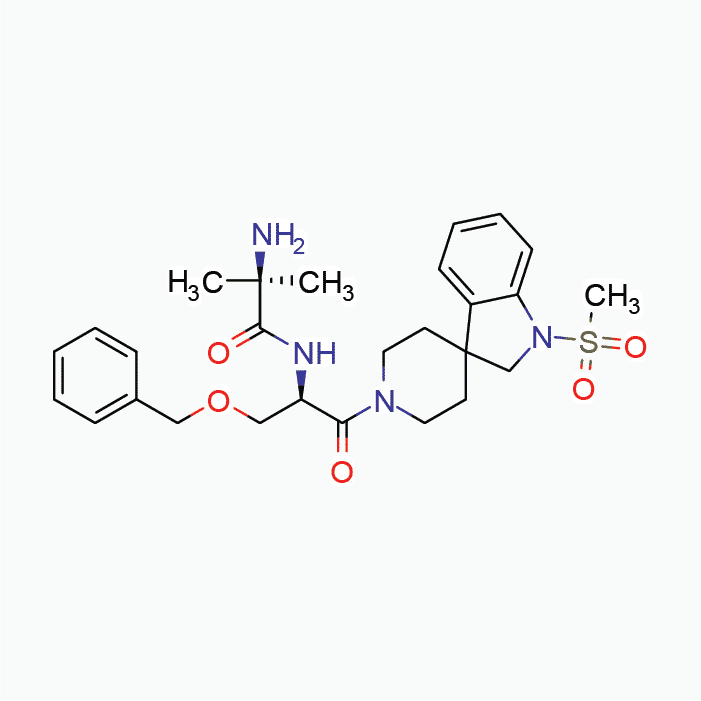
MK677 Solution, 750mg (25mg/mL)
AUD $149.00
Clinical research suggests that MK677 may have the ability to;
✓ Increase muscle mass by boosting production of IGF-1.
✓ Prevent muscle wastage even during fasting.
✓ Accelerate reduction of body fat.
✓ Improve skin, hair and nails.
✓ Improved sleep.
Note: Products are for laboratory research use only. Not for human use. Reference Materials are not therapeutics and we do not sell to patients.
In stock
| 1 | 2-4 | 5-9 | 10-19 | 20+ |
| AUD $149.00 | AUD $146.50 | AUD $144.00 | AUD $139.00 | AUD $129.00 |
| CAS | 159752-10-0 |
| Molar Mass | 624.77 g/mol |
| Chemical Formula | C27H36N4O5S |
| IUPAC Name | 2-amino-2-methyl-N-[(2R)-1-(1-methylsulfonylspiro[2H-indole-3,4′-piperidine]-1′-yl)-1-oxo-3-phenylmethoxypropan-2-yl]propanamide;methanesulfonic acid |
| Synonyms | Ibutamoren, MK-677, MK-0677, MK677, L-163,191, L163191, Nutrobal |
| Storage | Room temperature |
| Country of Origin | USA |
| Standard | 25mg/mL ±10% |
| Terms of sale | This material is sold for laboratory research use only. Terms of sale apply. Not for human consumption, nor medical, veterinary, or household uses. Information presented is based upon evidence found in clinical studies. Please familiarise yourself with our Terms & Conditions prior to ordering. |
Ibutamoren (MK677) has characteristics of HGH human growth hormone. It works as an oral secretagogue causing the body to increase its own growth hormone and IGF-1 levels, by mimicking the GH stimulating Ghrelin.
The main benefit shown by studies is its ability to increase growth hormone and IGF-1 levels. This results in a number of different health benefits including, increase in fat free mass, better quality sleep, better hair skin and nails, fat loss, increase in basil metabolic rate, improvement in overall wellbeing.
In Vivo:
Studies of Ibutamoren (MK677) suggest dosage to be anywhere between 5-25mg per day. Higher dosages were shown to result in some water retention, which were not present at lower doses.
Studies and additional info:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2757071/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9329386
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8784075
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9467542
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10404019
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11238495
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11452249
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9349662
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1234282/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9238854
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19015485
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2757071/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3053958
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2757071/