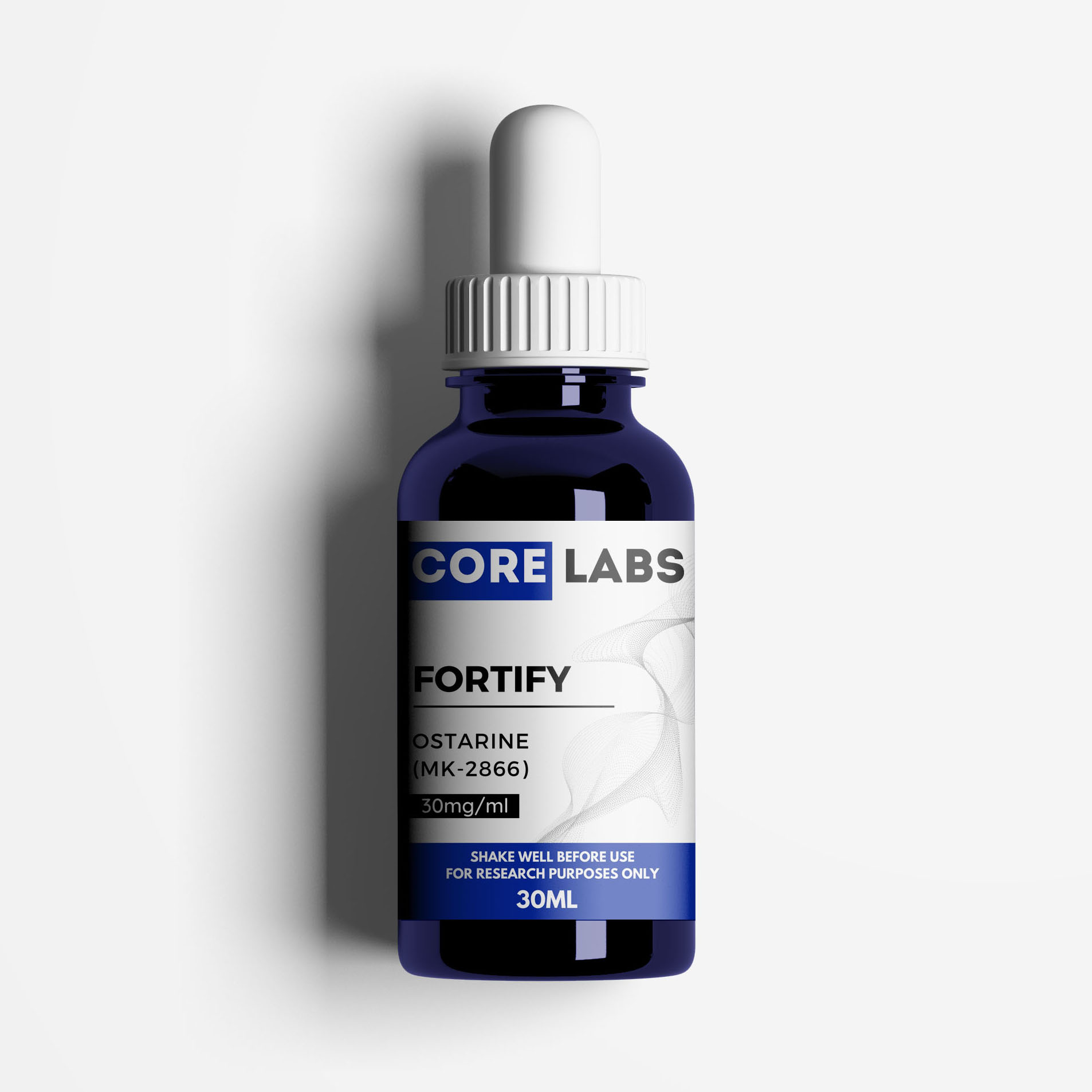
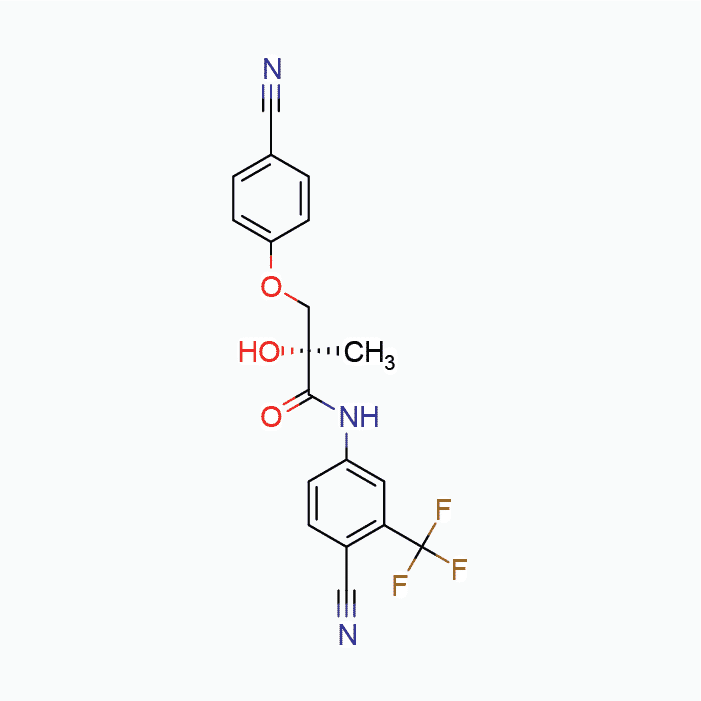
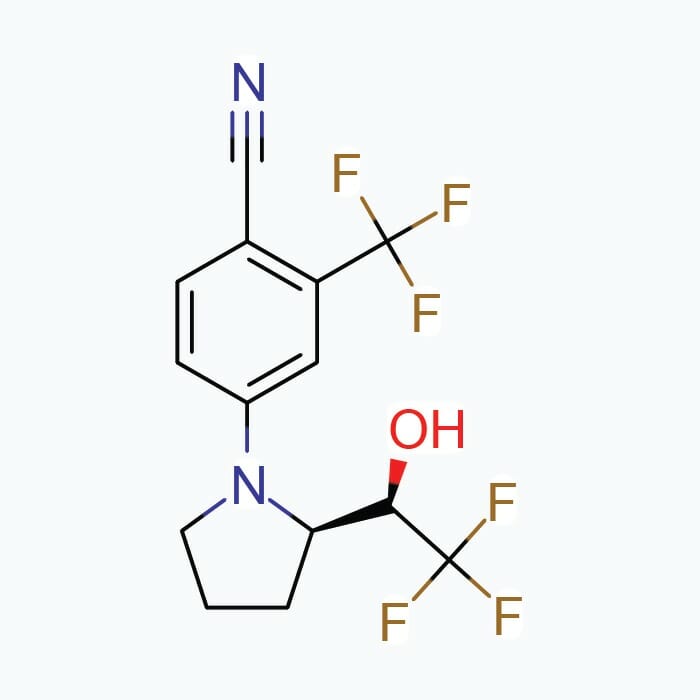
MK-2866 Solution, 900mg (30mg/mL)
AUD $149.00
Clinical research suggests that MK-2866 may have the ability to;
✓ Increase lean muscle mass and strength.
✓ Help with bone health and heart health.
✓ Wound healing, joint and other injury healing abilities.
✓ Improve well being.
Note: Products are for laboratory research use only. Not for human use. Reference Materials are not therapeutics and we do not sell to patients.
In stock
| 1 | 2-4 | 5-9 | 10-19 | 20+ |
| AUD $149.00 | AUD $146.50 | AUD $144.00 | AUD $139.00 | AUD $129.00 |
| CAS | 841205-47-8 |
| Molar Mass | 389.33 g/mol |
| Chemical Formula | C19H14F3N3O3 |
| IUPAC Name | ((2S)-3-(4-cyanophenoxy)-N-[4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide) |
| Synonyms | Ostarine, Enobosarm, GTx-024, MK-2866 |
| Storage | Room temperature |
| Country of Origin | USA |
| Standard | 30mg/mL ±10% |
| Terms of sale | This material is sold for laboratory research use only. Terms of sale apply. Not for human consumption, nor medical, veterinary, or household uses. Information presented is based upon evidence found in clinical studies. Please familiarise yourself with our Terms & Conditions prior to ordering. |
Ostarine (MK2866) was first developed to prevent muscle wastage in cancer patients and people with osteoporosis. Ostarine (MK2866) works by binding to the Androgen Receptor, increasing protein synthesis and altering the expression of genes. It almost exclusively exerts its anabolic effects on the muscle tissues and minimizes muscle atrophy, most notably during recovery periods from surgery and injuries. For this reason it can be favoured for its ability to heal muscle injuries due to its healing properties.
Ostarine (MK2866) is highly anabolic, even at moderate doses making it very effective at building lean mass gains.
In Vivo:
Studies of Ostarine (MK2866) suggest dosage to be around 30mg per day.
Studies and additional info:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2602589/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2039881/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2811355/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2039881/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2072878/